Blog title will be here.
Blog CategoryDatat non proident qui offici.hafw adec qart.
Geothermal (or Geo-exchange) is a type of HVAC System (Heating, Venting, and Air-Conditioning).
Geothermal is the most efficient Air-conditioning system because the ground temperature stays stable and has no regard for the above ground ambient temperature.
Geothermal Heat Pumps draw energy out of the ground which stays relatively constant year round.
In India, a tremendous amount of solar energy is available. The system combination of solar thermal collectors and heat pumps is a very attractive option for increasing the renewable energy usage at worldwide level for heating and domestic hot water preparation.
According to the Global Cooling Prize report2 the direct and indirect GHG emissions from RACs alone could contribute to a 0.50C increase in global warming by 2100. To address the rising cooling-related emissions, India has launched the India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) in 2019 which envisions to reduce, against the business-as-usual scenario, cooling demand across sectors by 20% to 25% by 2037-38, reduce refrigerant demand by 25% to 30% by 2037-38, and reduce cooling energy requirements by 25% to 40% by 2037-38.
Use of GSHP’s in India
GHP is effective in all kind of climate zones or can be deployed anywhere in India on 24 x 7 basis.
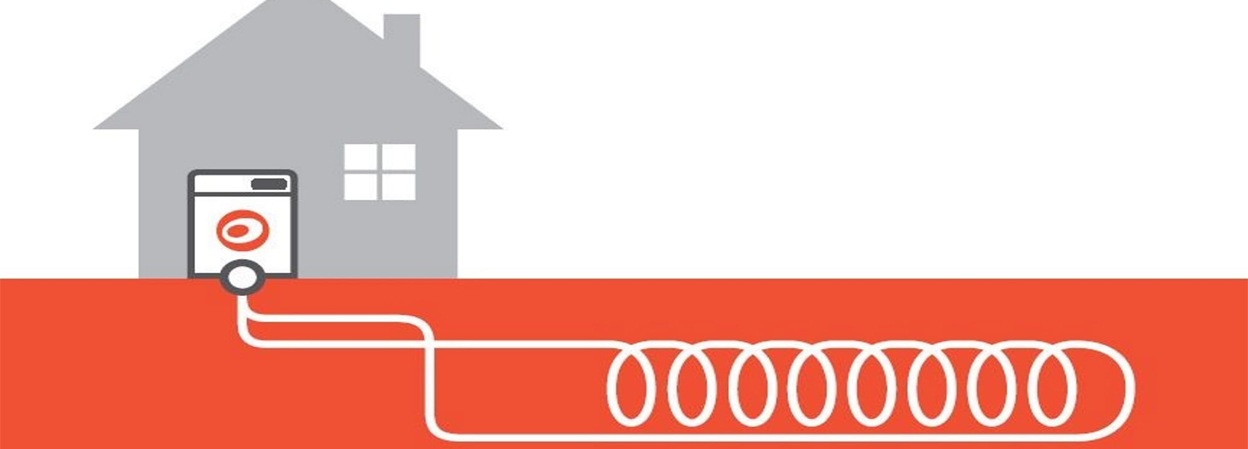
Heating: Earth's heat (the difference between the earth's temperature and the colder temperature of the air) is transferred through the buried pipes into the circulating liquid and then transferred again into the building.
Cooling: During hot weather, the continually circulating fluid in the pipes 'picks up' heat from the building - thus helping to cool it - and transfers it into the earth.
Use of GSHP can bring down substantially consumption of expensive electricity cost which is in the range of Rs 8-10 per unit at present.
The content of the course may be subject to change. Curriculum content is provided as a guide. The course consists of four core modules:
Overview of Ground‐Source Heat Pump (GSHP) Systems
A complete GSHP system includes both the ground loop and the building system. One should be able to understand the trade-offs in design decisions which affect the performance of a building and hold an understanding of how design decisions affect construction costs and have a sense of the percentage of the total mechanical system costs.
Design of Ground‐Source Heat Pump Systems
Step design process, including instruction using provided software for Ground Heat Exchanger Sizing, Pump Calculations, AHRI test data corrections to design conditions, and more. Design for closed‐loop vertical ground heat exchanger and closed‐loop surface water heat exchanger connected to a commercial building.
Ground Source Heat Pump Systems: Special Topics
YOU WILL BE ABLE TO:
Learn the procedures for surface water (closed-loop) heat exchanger and heat exchanger sizing using the software.
Gain an understanding of design considerations, including load imbalance, for ground-coupled heat exchangers in cold v. warm regions.
Understand the project cost impacts of certain design decisions.
and other available resources to improve and expedite GSHP designs.
Development of Ground‐Source Heat Pump Systems
Research Associate, IIT Roorkee
Ex. Senior Research AssociateSenior Research Associate
Centre for Nano and Material Sciences
PhD in Perovskite Solar Cell
University of Calcutta
M.Tech in Materials Science and Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
M.Sc (Physic), Civil Engineer
Certified Solar Trainer
12 years Experience in Training at Institute of Solar Technology